Why do AI search rankings fluctuate?
Traditional search has had “algorithm updates” since the beginning. These were large scale changes to the ranking factors, priorities, black hat mitigation, and other underlying rules of how Google set the rankings across their entire ecosystem.
Without a set schedule, you could still rely on updates being rolled out once or twice a year at most.
Understanding the pieces at play will help make the fluctuations make more sense and guide you in your content and optimization efforts.
In comparison, AI search responses are a lot more volatile, with updates seemingly happening constantly.
It’s tempting to think that these are wholly random, and out of our control (or at least our responsibility to manage), but there’s some very clear foundational patterns driving these changes.
Understanding the pieces at play will help make the fluctuations make more sense and guide you in your content and optimization efforts.
Related: Some argue that AI search can’t be optimized because it’s “too random.” We’ve written a complete guide debunking this myth → The Myth of AI Search Unoptimizability
Related: Despite fluctuations, the underlying source set is surprisingly stable. Learn how to choose the right questions to track → What Questions Should You Track?
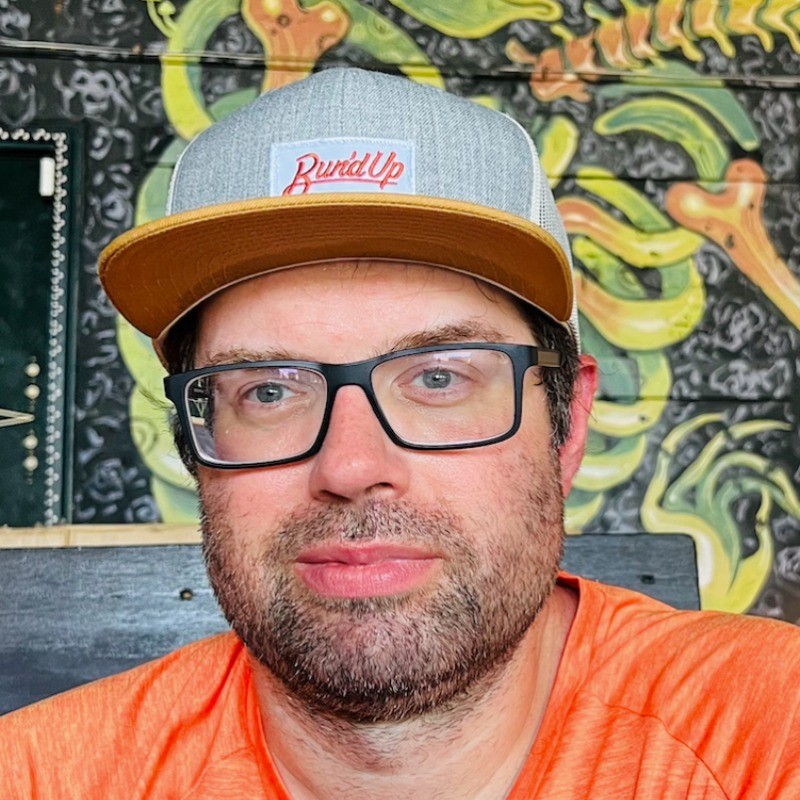
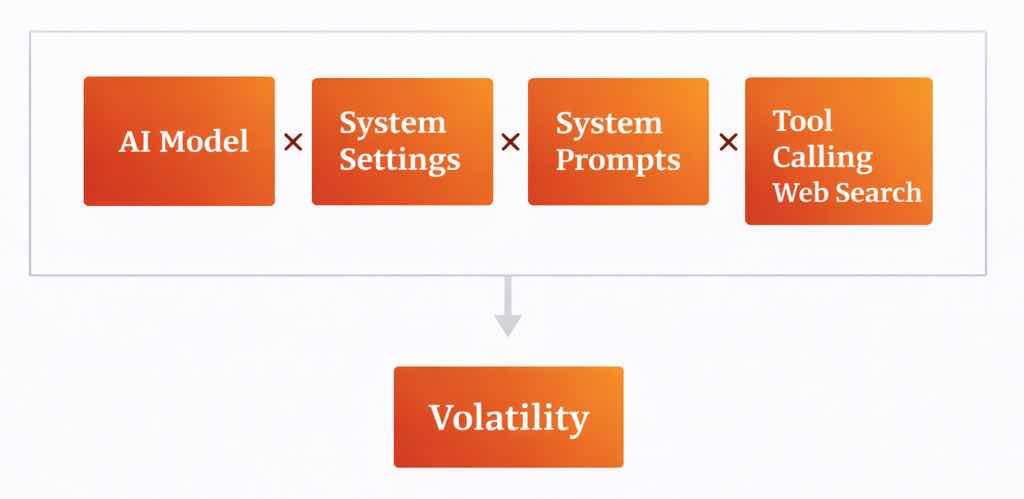
The four systems influencing AI search results
To understand why AI search seems so random, you first need to know how it works. What you see from an AI query comes from three different systems. Each can be updated on its own, and these updates often aren't public.
| System | Description | Update Frequency | What It’s Like |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. AI Model | The actual AI model trained based on a specific dataset with a cutoff date when they ended data collection. These are the big versioned model number updates that get press releases and announcements. | Infrequent (months to years) | Like a car’s engine - it powers the vehicle and sets hard limits on what’s possible |
| 2. System Settings | Underlying configuration settings (like temperature or top_p) used by the AI services to influence how the model responds. These can be updated instantly without retraining the model. |
Frequent (can change daily) | Like a car’s performance settings, allows for rapid adjustments to behavior |
| 3. System Prompts | Hidden instructions that control how the AI behaves and what it recommends. These can be updated instantly without retraining the model. | Frequent (can change daily) | Like a car’s steering wheel - allows for rapid adjustments to direction |
| 4. Tool Calling Web Search | Live search engine results that AI services pull in and filter for current information beyond the model’s cutoff date. | Infrequent (months to years) | Like attaching a trailer to the car - adds functionality and use cases as needed |
If any of the above change you're going to get a significantly different response.
1. AI Models update a lot more than you think
Going strictly by press releases and hype you’d be forgiven for thinking that AI models are updated once a year or so. For example, here’s the major releases from OpenAI:
- ChatGPT 3.5 (November 2022)
- ChatGPT 4.0 (March 2023)
- ChatGPT 5.0 (August 2025)
But in reality, AI models are updated much more frequently. Below is a snapshot of just the updates to the ChatGPT 4o model (from OpenAI’s documentation):
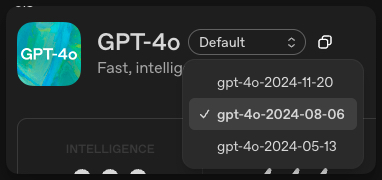
And that’s not counting ChatGPT 4.1 which was another release in the same series.
Looking over the entirety of “ChatGPT” the true data + model updates is much closer to monthly than annually.
2. System settings and volatility
Another major source of volatility comes from system settings updates. System settings are the underlying configuration parameters (like temperature, top-p, output length) that control how the AI model responds.
Hidden configurations can change overnight and dramatically affect brand visibility, even when nothing else changes.
These technical settings can be updated instantly without retraining, and services constantly adjust them to balance cost, speed, quality, and safety. The same model with different settings can produce completely different results.
For example, higher temperature values make responses more random and creative, which means more variation in which brands get mentioned. Lower output length limits mean fewer brands fit in the response. Enabling or disabling grounding with search can completely change whether your traditional SEO matters.
Learn more: For a deep dive into system settings like temperature, grounding, and output length, and what they mean for your visibility → System Settings and AI Search
3. System prompts and volatility
A big reason for volatility comes from updates to system prompts. These are hidden instructions that tell AI services how to act and what to recommend.
Unlike the AI model, system prompts can change instantly without retraining the entire model. So, your visibility can shift overnight when these hidden instructions are updated.
For instance, a new instruction like “prioritize sources from the past 6 months” could suddenly boost competitors with recent news. Or, a rule to “mention pricing when recommending products” might leave you out if your prices aren’t clearly shown.

Learn more: Want to dive deeper into how system prompts affect AI search rankings and what leaked prompts tell us? Check out our full guide → System Prompts and AI Search SEO
4. Tool calling web search and volatility
“Tool calling” is what AI models do when they need to pull in additional help from outside sources for information or tasks that aren’t handled by the model itself.
For instance, you can’t train a model to know what the weather is going to be tomorrow.
So in cases like this the model (like in the screenshot of ChatGPT below) will call out to an external “tool” to get that information.
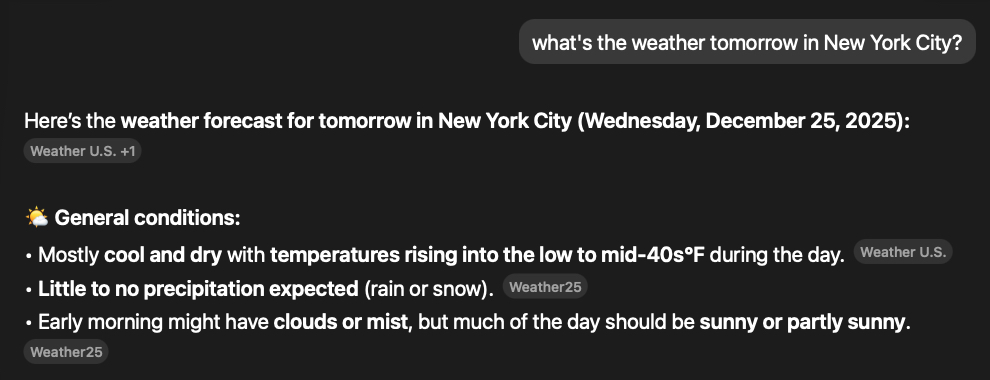
If the model decides that doing a web search is the best way to answer a question, it will call out to the web search tool to get the information, at which point you’re back to traditional search results (albeit filtered via the model)
How to handle volatility in AI search
Some people look at the above and despair. They think it’s too complicated or impossible to optimize for, but I genuinely take this another way.
- There’s opportunity here as each shift and change is a new chance for your brand to be mentioned.
- The volatility is churning up a wider variety of brands and sites that have gotten really calcified in traditional search results.
- While the volatility is high, your strategy should _not_ be reactive. A steady constant push of your messaging, content, and brand sentiment building efforts should be the norm.
- We’re here to help. We’ve specifically built Knowatoa to help you track your visibility in AI search and to help you optimize for the changes. Sign up for a free account to get started.
