Why Search Volume is still Search Volume
A mistake we see a lot of people make is thinking that “AI search volume” is some small separate subset of traditional search volume.
It’s not.
And to be clear, this isn’t me saying this, Google made the decision that right now every single keyword that people type into a search box is fair game for:</mark>
"A mistake we see a lot of people make is thinking that 'AI search volume' is some small separate subset of traditional search volume. It's not."
Search Volume has always been more of a vibe than a science
There’s a lot of unknowns with marketing and SEO, so it would be nice to think of search volume as a concrete snapshot of user behavior.
But search volume data:
- Is based on search advertising data, so there’s some level of skepticism about the potential self-serving nature of the data.
- Has always been an approximation. It’s more like a moving average that’s tweaked based on historical data and trends (seasonality, etc.)
- Is best treated as a relative metric of popularity: you can be fairly confident that a term with 10,000 searches a month is most likely getting roughly 10x that of a search with 1,000 searches a month. Even if both those numbers are often off by quite a bit.
- Is frequently wildly wrong for low volume search terms and newer topics.
How do I know how much search volume there is in ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity?
Because most search volume data is based on advertising and the AI services are still mostly burning VC dollars to get users to use their services (and not yet pivoted to selling ads), we don’t have much in the way of detailed search volume data from the AI services.
That being said, we do have really good data that:
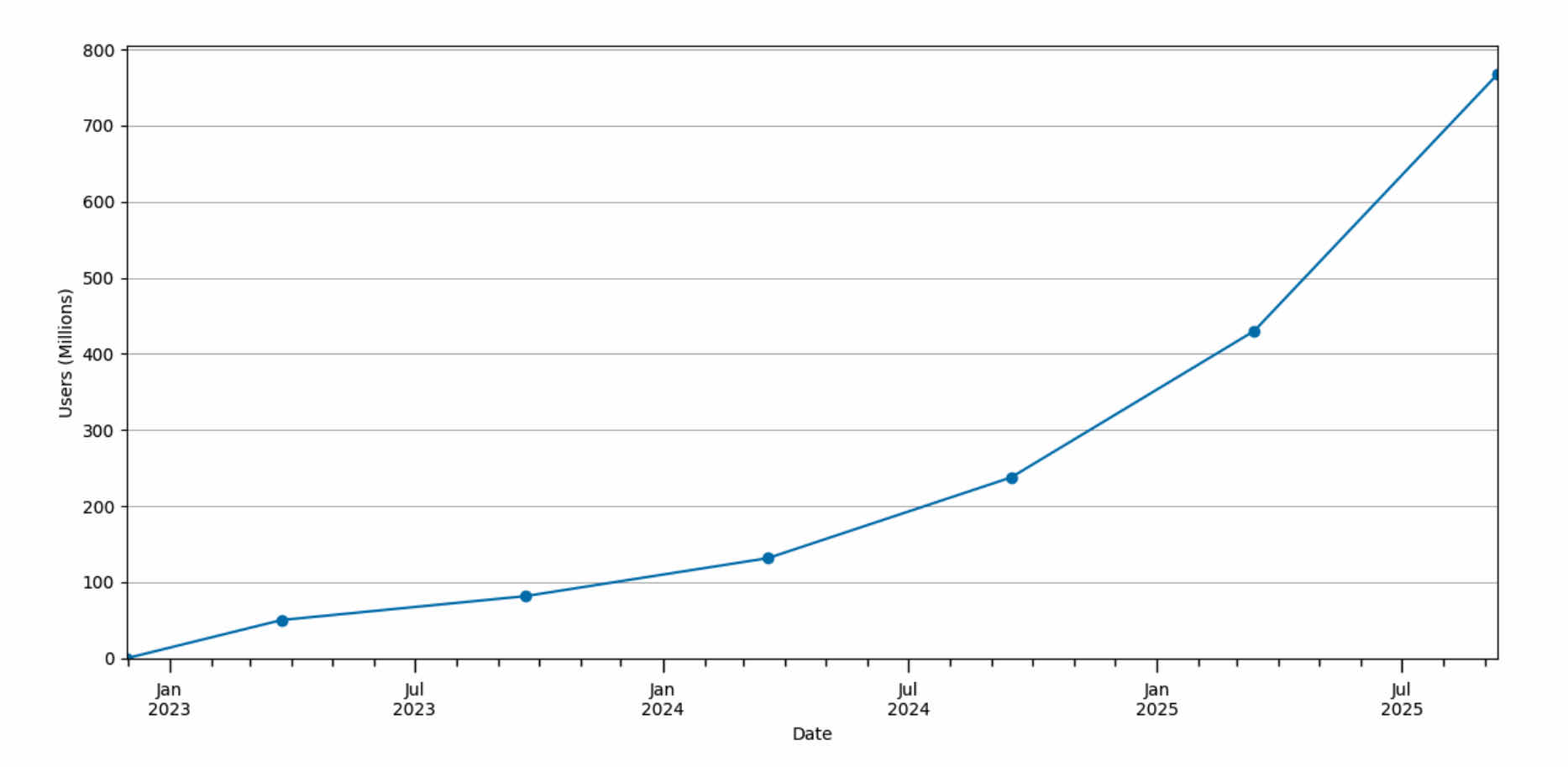
1. More people are using AI services every month.
~10% of all adults in the world are using ChatGPT every month.
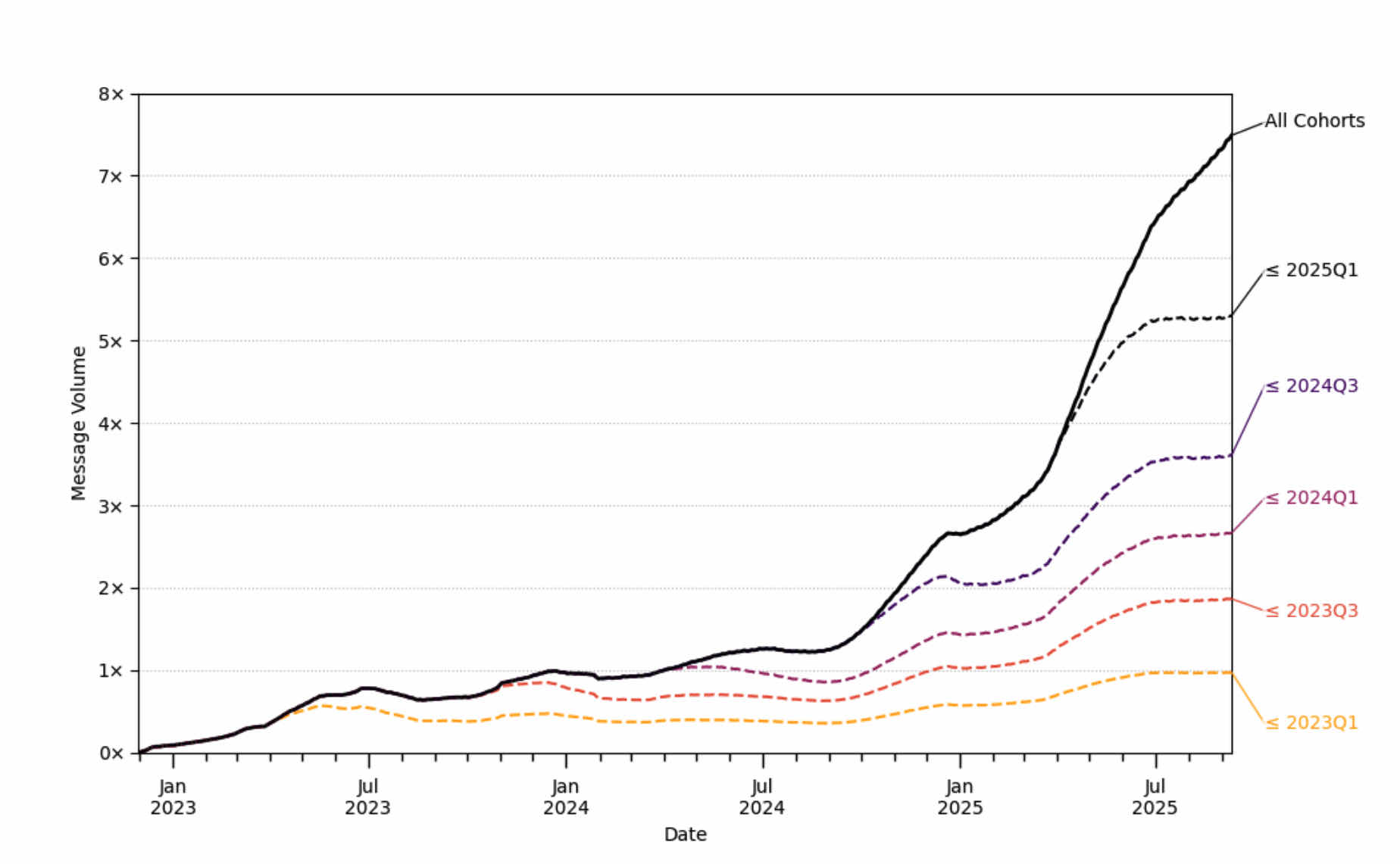
2. AI use is very “sticky”.
People are consistently using AI services more over time (asking more questions, more use cases, more hours per month).
3. People are using AI services for search like tasks (~51% of usage).
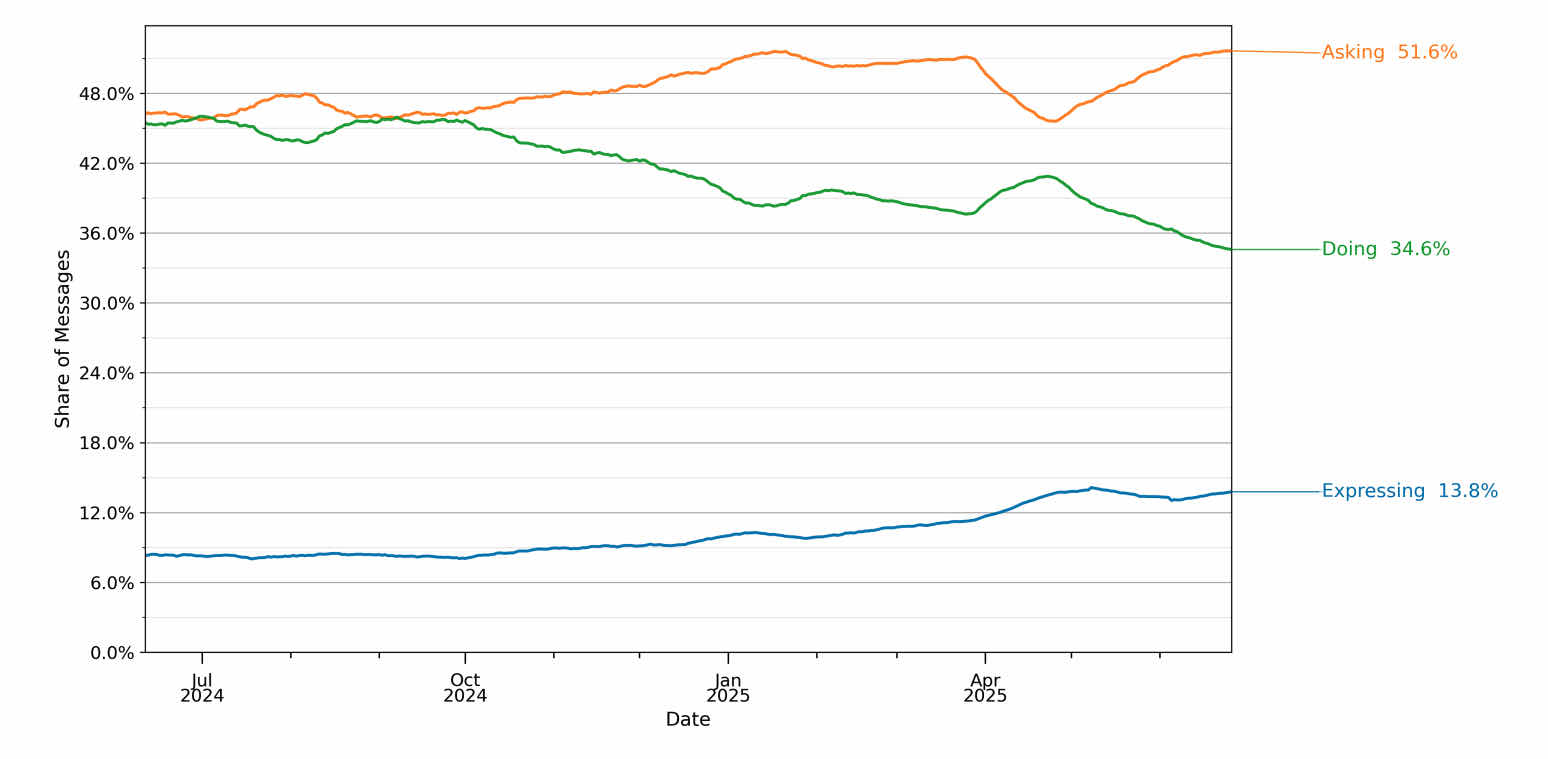
4. People are using AI services for higher value searches
A lot of traditional search volume is very low value. It’s people looking up definitions, navigating to sites they already know about. But AI services are being used for more and more complicated decision making tasks that blend “search” and “decision making” and “advice” into a single task.
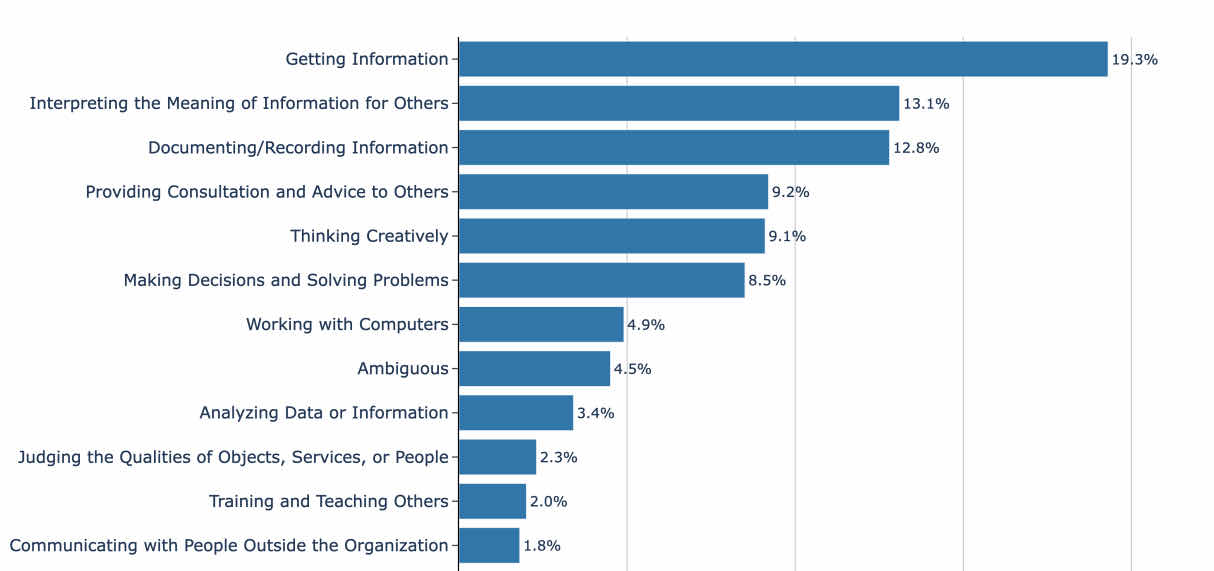
Source: "How People Use ChatGPT" (Chatterji et al., 2025)
How People Use ChatGPT. OpenAI, Duke University, and Harvard University. September 15, 2025.
Download paper (PDF)
Search is Fracturing
If there’s one clear trend it’s that search is getting a lot less monolithic:
- Google themselves are splitting search into multiple “surfaces” (AI Overviews, AI Mode, Gemini)
- AI services like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity are gaining increasing market share
- People are using AI services for search like tasks that blend search with the tasks they are trying to accomplish.
All of this is making it more and more difficult to categorize search volume. At Knowatoa, we’re trying to move beyond just categorizing search volume and into understanding the actual search tasks that people are performing.
We focus on the questions that drive value for your business wherever they are asked and however often. This is a more modern and powerful way to think about the underlying search drivers.
Next Step: Apply these concepts using the B.I.S.C.U.I.T. framework → Explore the B.I.S.C.U.I.T. Framework
